Theory of Indices
The 3 laws of indices for positive integers :
- am x an = am+n
- am ÷ an = am-n [m>n]
- (am)n = amn
The law of index for zero (0) :
20 = 21 ÷ 21 [by law of indices for positive integer]
In general :
21 ÷ 21 = 1
\ 20 = 1a0 = a1 ÷ a1 [by law of indices for positive integer]
= an ÷ an = 1
\ a0 = 1
The law of index for negative integers :
2-1 = 20 ÷ 21 [by law of indices for positive integer]
In the same way
= 1 ÷ 2 = ½
\ 2-1 = ½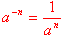
The law of index for fractions :
4½ = ?
4½ x 4½ = 41
\ (4½)2 = 4 [by law of indices for positive integer]
\ Ö4 = 4½In general :
= ?
x
x
= 8
\ ()3 = 8 [by law of indices for positive integer]
\=
\
\
In general :
= ?
or =
( )2 [by law of indices for positive integer]
[by law of indices for positive integer]
= 22 = = 4 = 4
or